- Traverse City, MI |
-
West: W Front St:
(231) 944-6541
-
| Central: Munson Ave :
(231) 421-9300


The vertebrae in the spinal column are separated by spongy discs made of collagen tissues.
They also have a jellylike center called the nucleus. These discs serve as shock absorbers when the spine is flexed. They support the vertebrae and allow for bending.
When these intervertebral discs become too compressed, they bulge out of the vertebrae. The condition is called bulging disc, which can lead to pain and immobility.

Although both conditions affect the discs in the spinal canal, and individuals experiencing either can report similar symptoms, bulging discs and herniated discs have a key difference.
With bulging discs, the disc sags and bulges outward. A herniated disc, on the other hand, means that there is a tear in the inner nucleus which causes a leak into the spinal canal.
This means that bulging disc only affects the outer, tougher cartilage of the disc, while the herniated disc affects the center as well. People with the latter condition may also experience more severe pain compared to the former, because the nerves in the spinal cord may be involved.
People who have bulging discs may experience the following symptoms:
Back pain that is noticeably worse when the individual moves or walks
Back muscles experience spasms
Numbness or general weakness in the legs and feet
Reduced mobility in the lower extremities
Reduced bowel and bladder control
Pain along the sciatic nerve or sciatica
Reduced overall coordination

Aging – The jellylike nucleus in the disc tends to wear away as people age.
Physical Activity – Heavy lifting, repetitive forceful motions, repetitive bending and twisting, and other activities that put a lot of stress on the back may eventually wear out the nucleus of spinal discs and lead to this condition.
Trauma – Injuries sustained during an accident may damage and weaken the intervertebral discs. This may lead to bulging disc.
Posture – Poor posture when sitting, standing, driving, or working for sustained periods of time can eventually lead to weakness and bulging of the discs.
Poor motion Above or Below- If the hips and upper spine don't move enough the disc will move more, resulting in a bulge or herniation.
Since in most of the cases of bulging discs there is a progressive and gradual presentation of symptoms over time, individuals can get their condition diagnosed and treated early. This involves conservative treatment options such as the following:
Medications – anti-inflammatory drugs can be recommended, especially during flare-ups of the symptoms. These reduce swelling and relieve pain.
Steroid Injections – If there is significant nerve pain, doctors may also recommend steroid injections to manage the inflammation and pain.
Doctors may also recommend a surgical option called lumbar decompression if the bulging disc has progressed enough to also cause lumbar stenosis. This procedure decompresses the spinal canal which effectively reduces pressure on the nerve and relieves pain but only works 50% of the time because the root dysfunction was not addressed.

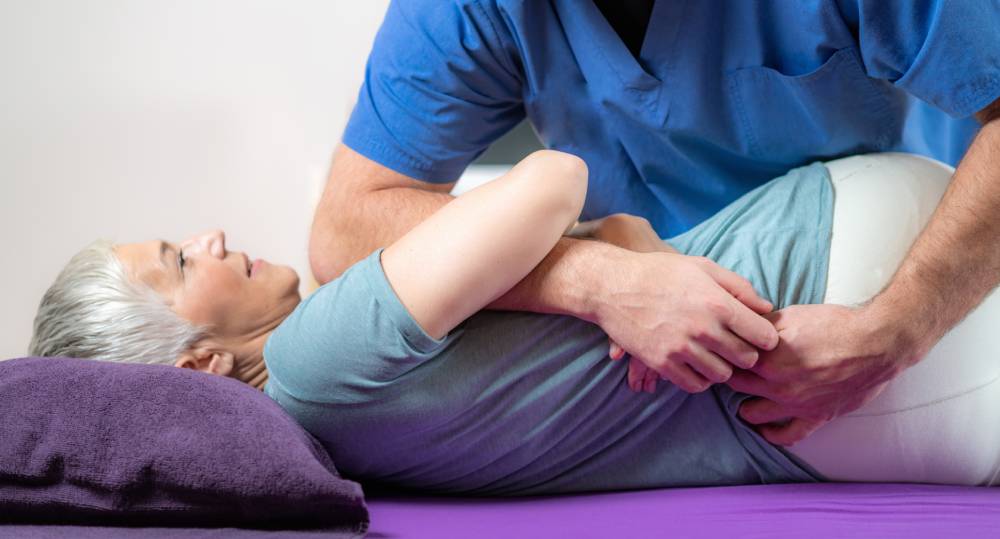
While the traditional treatment options mentioned above may be effective in managing the pain in the short-term, they do not necessarily address the underlying cause of the bulging disc.
At Superior Physical Therapy, we do not only look at the site of the pain. We recognize that the body is made up of several interconnected moving parts and that an issue with one of these parts may lead to pain and other symptoms in another part.
Bulging discs, for example, may be caused by lack of movement in the areas above and below the spine.
To learn how science supports physical therapy for disc bulge click here.
Using this Superior Method we are able to correctly identify the problem and find more lasting solutions. We also offer the following treatment options:
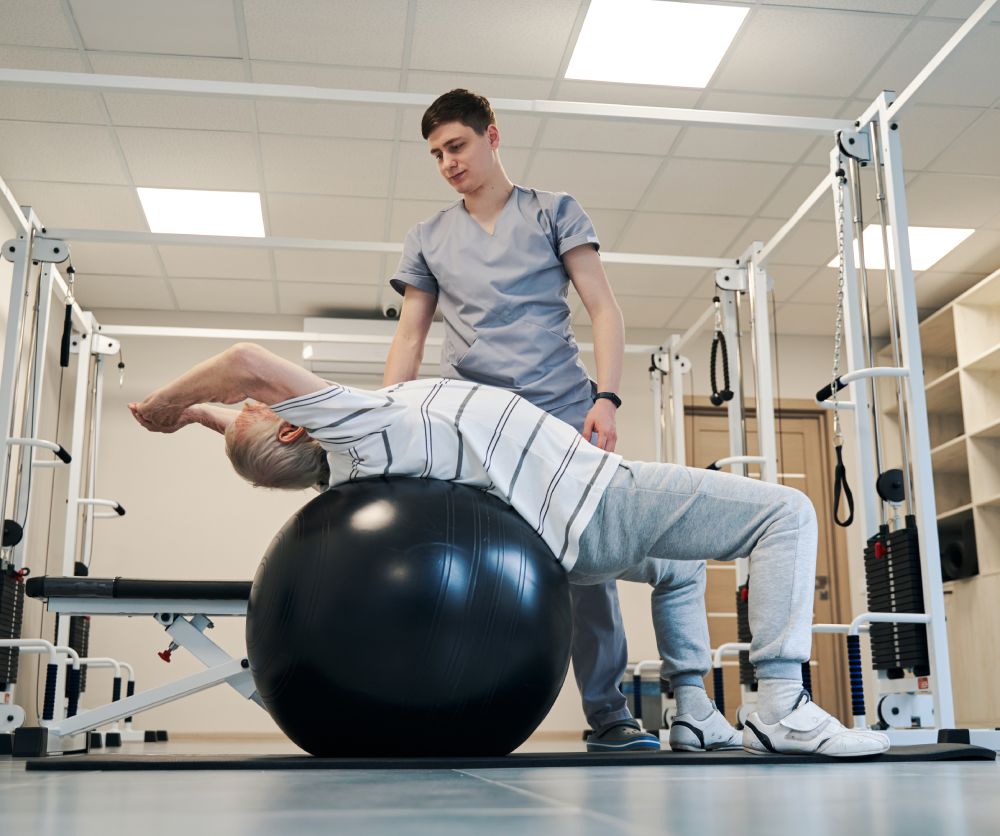
A series of targeted exercises can concentrate the symptoms in the middle line of the body and eventually alleviate pain. This offers long-term solutions to pain and weakness in the back.
The most important element of healing is identifying the cause. The cause is a movement disorder somewhere else in the body that is creating more stress in the injured area than the tissue can handle. A full body movement assessment is the most important aspect in finding the true cause. This involves assessing how mobile and stable the areas above and below the injured tissues are. Once the dysfunctional areas are identified the physical therapist can then prescribe home treatments to fix the problem areas.
In order to improve motion in the dysfunctional areas that are causing the increased stress on the painful injured tissues the most effect way to make a change in the body is to have a physical therapist use their hands to facilitate the proper motion while you are moving at the same time. This helps improve the path the body takes in order to reduce stress and tenson on the injured area.
Using mechanical vibrations that penetrate deep into muscle tissue, circulation and lymphatic flow are improved. Tissue regeneration is also promoted. The lactic acid cycle is also improved, eliminating one common cause of pain.
Find out which of these treatment options are the best fit for you when you get into a quick and easy discovery call with our own Dr. Andrew Gorecki.
Begin your journey to lasting relief against bulging disc when you dial 231.944.6541 or email info@thesuperiortherapy.com. Our consultation is FREE.
Back pain injections, such as epidural injections or nerve blocks, can be safe if done by a trained medical professional. However, as with any medical procedure, there is always a risk of side effects and complications, such as infection or nerve damage. Your doctor will be able to advise you on the risks and benefits of back pain injections and help you make an informed decision.
Back pain is a common symptom during pregnancy, and can be caused by a number of factors, including hormonal changes, weight gain, and the increased pressure on the spine from the growing uterus. Mild to moderate back pain can often be managed with simple self-care measures, such as exercises, heat therapy, and good posture. Severe or persistent back pain should be evaluated by a doctor to rule out more serious conditions.
Back pain and stomach pain can be related in some cases, for example, if the back pain is caused by a condition affecting the abdomen, such as a kidney stone or a bladder infection. However, it's important to seek medical attention to determine the cause of the symptoms, as they may be caused by a serious condition.
Back pain during contractions can occur during labor and delivery, as the uterus contracts and puts pressure on the lower back. Some women also experience back pain during early labor, as the baby's head begins to engage in the pelvis.
Back pain and chest pain can be related in some cases, such as if the back pain is caused by an injury to the chest or rib cage. However, chest pain can also be a symptom of serious conditions, such as heart attack or lung problems, so it's important to seek medical attention to rule out these possibilities.
Back pain is not usually a sign of pregnancy, and there are many other symptoms that are more commonly associated with pregnancy, such as missed periods, nausea, and fatigue. If you think you might be pregnant, it's important to take a pregnancy test and see your doctor for confirmation.
Back pain and constipation can be related in some cases, as the increased pressure on the abdominal muscles from constipation can cause pain in the lower back. Treatment for constipation can help relieve the back pain.
Back pain can be a symptom of pregnancy, but it's not always the case. Other common symptoms of pregnancy include missed periods, nausea, fatigue, and breast tenderness. If you're experiencing back pain and think you might be pregnant, it's important to see your doctor for confirmation.
Yes, back pain can cause chest pain, especially if the pain is caused by an injury or condition affecting the chest or rib cage. If you're experiencing chest pain along with back pain, it's important to seek medical attention to determine the cause.
Yes, back pain can cause nausea, as the pain can interfere with normal digestive function and trigger feelings of nausea. If you're experiencing back pain and nausea, it's important to seek medical attention to determine the cause.
Yes, back pain can cause stomach pain, especially if the pain is caused by a condition affecting the abdomen, such as a kidney stone or a bladder infection. If you're experiencing both back pain and stomach pain, it's important to seek medical attention to determine the cause.
Yes, back pain can cause headaches, as the pain and stress can trigger tension headaches or migraines. If you're experiencing both back pain and headaches, it's important to seek medical attention to determine the cause and get appropriate treatment.
No, back pain is not a reliable sign of pregnancy. There are many other symptoms that are more commonly associated with pregnancy, such as
While back pain itself does not directly cause high blood pressure, the stress and anxiety that can accompany chronic pain can contribute to the development of high blood pressure. It is important to manage both conditions effectively to improve overall health.
In some cases, back pain can be a symptom of a more serious underlying condition such as cancer, especially when it is accompanied by other symptoms such as weight loss, fatigue, or fever. However, it is important to note that most cases of back pain are caused by non-cancerous conditions such as muscle strain or injury.
Back pain can occur due to a variety of reasons such as injury, overuse, aging, arthritis, a herniated disc, or conditions affecting the bones, muscles, or nerves in the back. It can also be a result of poor posture, sedentary lifestyle, or a combination of factors.
Back pain can happen as a result of physical strain, injury, or a condition that affects the bones, muscles, or nerves in the back. This can include activities such as heavy lifting, repetitive motions, or prolonged sitting, as well as underlying conditions such as arthritis, spinal stenosis, or osteoporosis.
The best course of treatment for back pain will depend on the underlying cause. Common options include over-the-counter pain medication, physical therapy, heat therapy, massage, chiropractic care, and in some cases, surgery. In addition, lifestyle changes such as maintaining proper posture, engaging in regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight can also help alleviate back pain and prevent it from recurring.
Back pain can have a significant impact on daily activities and quality of life. It can limit mobility, cause difficulty with work or personal tasks such as standing, sitting, or walking for prolonged periods, and contribute to stress and anxiety. Chronic back pain can also lead to depression and decreased physical and emotional well-being.
Back pain relief options vary, but common remedies include pain medication, physical therapy, hot or cold therapy, exercise, massage, chiropractic care, and in some cases, surgery. In addition, lifestyle changes such as maintaining proper posture, engaging in regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight can also help alleviate back pain and prevent it from recurring.
Back pain can have a significant impact on daily activities and quality of life. It can limit mobility, cause difficulty with work or personal tasks, and contribute to stress and anxiety. Chronic back pain can also lead to depression and decreased physical and emotional well-being. In addition, it can make it difficult to participate in leisure activities and maintain relationships, leading to decreased overall satisfaction with life.
It is difficult to determine the specific type of back pain without a thorough evaluation by a medical professional. A doctor may use various diagnostic tests, including X-rays, MRI, and physical examination, to determine the cause of the pain.
Back pain can be caused by a variety of factors, including injury, overuse, aging, arthritis, a herniated disc, or conditions affecting the bones, muscles, or nerves in the back. It can also be a result of poor posture, sedentary lifestyle, or a combination of factors.
Back pain can feel like a dull ache, sharp stabbing pain, or a burning sensation, depending on the cause. The location and intensity of the pain can also vary, and it may be accompanied by muscle spasms, stiffness, or tenderness.
Back pain refers to discomfort, soreness, or ache in the lower or upper back region.
The severity and frequency of back pain required for disability benefits vary and depend on several factors, such as the type of work, medical conditions, and overall health. A doctor can evaluate if back pain qualifies for disability.
A diagnosis of the specific type of back pain can only be determined by a medical professional after a thorough evaluation, including a physical examination and possibly imaging tests.
Severe or worsening back pain, accompanied by symptoms like fever, numbness, tingling, or loss of bladder or bowel control, can indicate a serious underlying medical condition and should be promptly evaluated by a doctor.
Back pain can cause referred pain in other areas of the body, including the chest. This is because the nerves that serve the back also serve other regions. Chest pain should be evaluated by a doctor to determine the underlying cause.
Back pain is a common complaint during pregnancy due to the changes in weight distribution and increased stress on the lower back. It can be treated with simple measures such as rest, exercise, and proper posture.
Back pain can cause referred pain or radiculopathy (nerve pain) in the legs. This occurs when a nerve in the back is compressed or irritated.
Mild to moderate low back pain is common during pregnancy and usually improves with rest, exercise, and proper posture. However, if the pain is severe or persistent, a doctor should be consulted.
Back pain is a common issue that refers to discomfort or pain in the lower, middle, or upper back. It can be caused by a variety of factors including injury, strain, or underlying medical conditions.
Back pain that is so severe and persistent that it significantly limits a person's ability to perform essential daily activities and work may qualify for disability benefits.
Back pain can be considered serious if it is accompanied by other symptoms such as fever, weakness in the legs, loss of bladder or bowel control, or unexplained weight loss. In such cases, prompt medical attention is necessary.
Chest pain along with back pain can be a sign of various conditions, including heart disease, lung problems, and muscular or nerve issues. It is important to seek medical attention immediately if this type of pain is experienced.
Back pain during pregnancy is common due to the changes in a woman's posture and weight as the baby grows. Hormonal changes and pressure on the lower back from the growing uterus can also contribute to back pain during pregnancy.
Leg pain in addition to back pain can be a sign of various conditions, including sciatica, nerve compression, or spinal stenosis. In some cases, the cause may be related to the back, while in others it may be due to a separate issue in the legs.
Mild to moderate back pain during pregnancy is considered normal as a result of the physical changes and increased weight. However, it is important to speak with a healthcare provider if the pain becomes severe or persistent.
Back pain can be a symptom of a serious underlying condition, such as a spinal cord injury, nerve damage, or a serious infection. Severe or worsening back pain, accompanied by symptoms like fever, numbness, tingling, or loss of bladder or bowel control, should be promptly evaluated by a doctor.
Back pain can be a symptom of spinal cancer, but it is not always an indicator. A doctor should be consulted to determine the underlying cause of the back pain.
Severe or persistent back pain during pregnancy, especially accompanied by other symptoms like abdominal pain or vaginal bleeding, can indicate a complication and should be evaluated by a doctor.
Back pain can be considered too much if it interferes with daily activities and quality of life, or if it is severe and persistent. A doctor should be consulted to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
Back pain that moves from side to side may indicate a more serious underlying condition and should be evaluated by a doctor.
Back pain can cause referred pain in other areas of the body, including the abdomen, which can cause nausea. A doctor should be consulted to determine the underlying cause.
Back pain can be caused by many factors, including muscular strain, nerve irritation, or a more serious underlying medical condition. A doctor should be consulted to determine the cause of the back pain.
Back pain can get worse with prolonged sitting or standing, improper posture, heavy lifting, or other physical activities. It can also worsen with age or underlying medical conditions. A doctor should be consulted to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
Back pain is considered serious if it is accompanied by other symptoms such as fever, weakness in the legs, loss of bladder or bowel control, or unexplained weight loss. Prompt medical attention is necessary in such cases.
Back pain can be a symptom of cancer, but it is not always a definitive sign. Cancer-related back pain is usually accompanied by other symptoms such as weight loss, fatigue, and weakness. A doctor should be consulted if back pain persists or is accompanied by other symptoms.
Back pain during pregnancy should be concerning if it is severe, persistent, or accompanied by other symptoms such as vaginal bleeding or decreased fetal movement. In such cases, prompt medical attention is necessary.
Back pain is considered too much when it interferes with a person's daily activities and causes significant discomfort. If back pain is persistent or becomes more severe, a doctor should be consulted.
It is concerning if back pain moves from side to side as this may indicate a more serious underlying condition. If this type of pain is experienced, a doctor should be consulted for a proper evaluation.
Back pain during periods can be caused by various factors such as hormonal changes, muscle cramps, and changes in posture. The hormonal changes during menstrual cycles can cause inflammation and pain in the lower back.
Back pain is a common symptom of COVID-19, especially in severe cases. The reason behind it is still unknown but it could be related to the inflammation and pressure on the chest caused by the virus.
Back pain is a common experience during pregnancy as the body adjusts to the growing uterus, changes in posture, and weight gain. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can also cause ligaments to loosen and lead to back pain.
Back pain before periods can be a result of hormonal changes and muscle tension caused by PMS (premenstrual syndrome).
Back pain when sick can be caused by various reasons such as coughing, sneezing, or lying down for long periods. Also, some illnesses such as the flu or pneumonia can cause inflammation and pain in the back.
Back pain that comes and goes can be caused by various factors such as posture, lifestyle, physical activity, and certain medical conditions. Sometimes, back pain can be the result of an injury or strain that takes time to heal.
Back pain after an epidural can be caused by the insertion of the needle or due to nerve irritation. Some people may also experience soreness in the lower back from lying in one position for a long time during labor.
Back pain in early pregnancy can be caused by various factors such as hormonal changes, increased weight, and changes in posture. As the uterus expands and the body adjusts, the weight shift can cause lower back pain.
Back pain can go away, however, the timeline depends on the underlying cause and severity of the pain. Simple back pain can go away with proper treatment and self-care, while chronic back pain may require more comprehensive treatment and a longer recovery time.
In some cases, back pain can go away on its own with proper self-care and adequate rest. However, if the pain persists or becomes severe, it's best to seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause and find the appropriate treatment.
Back pain can go away, but the timeline for recovery depends on the underlying cause and severity of the pain. Chronic back pain may require long-term treatment and management, but with proper care, most people can experience a significant reduction in pain.
Back pain itself doesn't directly cause high blood pressure, but certain underlying conditions such as kidney problems, infection, or spinal issues can cause both back pain and high blood pressure.
Back pain can cause nausea in some individuals as a result of muscle tension, inflammation, or nerve irritation. In severe cases, underlying medical conditions such as a herniated disc or spinal stenosis can cause nausea and back pain.
Back pain from an epidural can go away, but the timeline for recovery depends on the individual and the severity of the pain. Some people may experience soreness and discomfort for a few days, while others may experience more significant pain that takes longer to subside.
Back pain can cause chest pain in some individuals, especially
